Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124

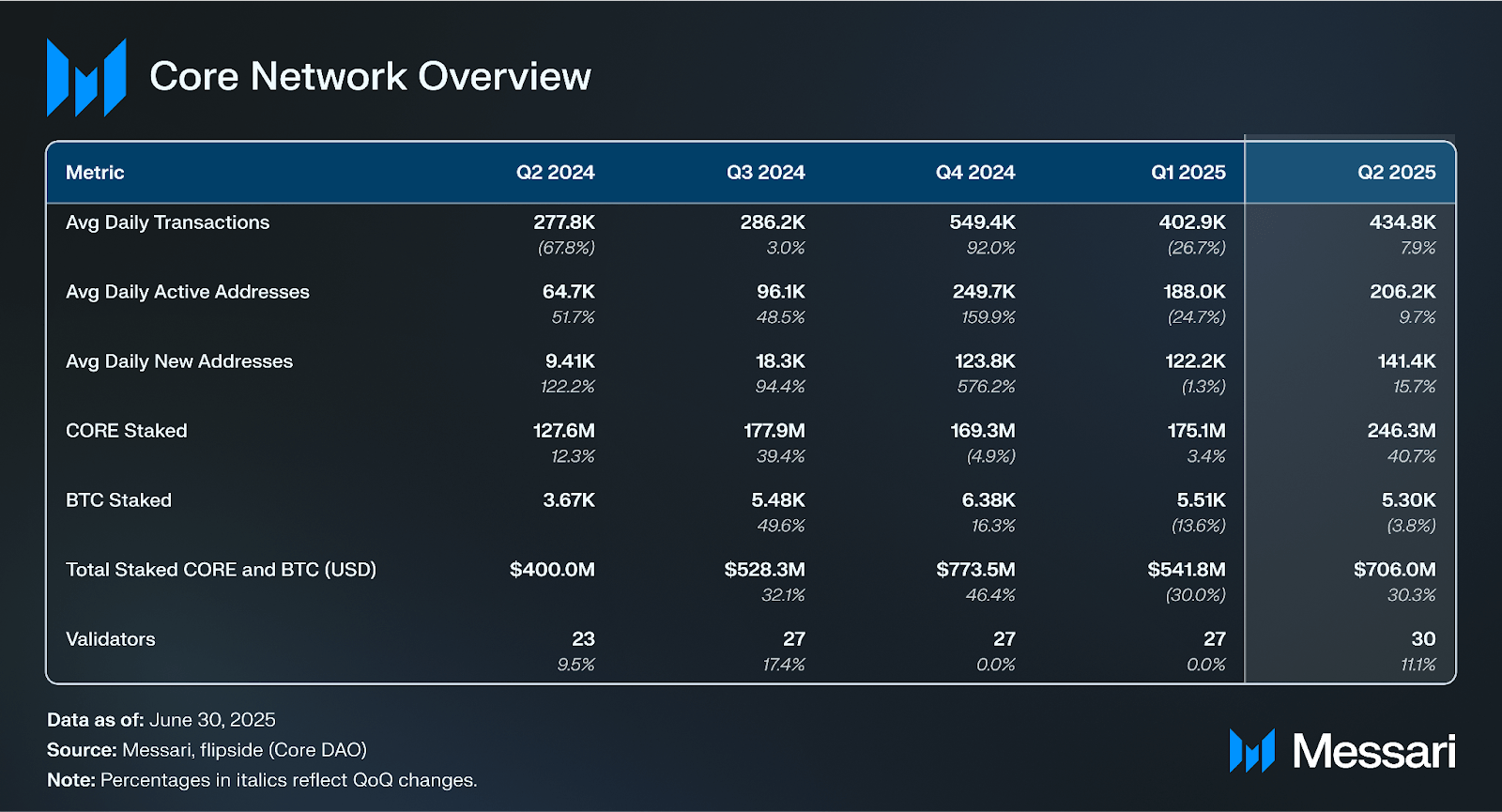
The Core blockchain (CORE) is a Layer-1 scaling and programmability solution for Bitcoin powered by its Satoshi Plus consensus, EVM execution environment, Bitcoin-based DeFi (BTCFi), and Core governance. Launched in January 2023, Core has built an ecosystem of Bitcoin-focused applications that inherit security from Bitcoin’s consensus resources (i.e., Bitcoin miners, etc.) wherever possible.
Core’s biggest differentiator from other Bitcoin layers (and merge-mining in general) is its Satoshi Plus consensus mechanism, a hybrid model of Delegated Proof-of-Work (DPoW), Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS), and Self-Custodial BTC Staking. Under DPoW, Bitcoin miners and pools delegate their hash rate to validators, contributing to Core’s consensus without requiring changes to Bitcoin’s base layer. Under DPoS, CORE tokenholders stake/delegate their tokens to select validators on Core.
Core introduced Self-Custodial BTC Staking in April 2024, offering consensus participation to BTC holders who lock their tokens on Bitcoin using absolute time locks. In return, holders receive voting power on Core, which they delegate to elect validators, earning BTC holders CORE token rewards. Core relayers monitor the BTC network for valid lockup transactions and forward approved ones to Core’s Consensus Engine. The DPoW hash, DPoS stake, and BTC stake contribute to a weighted score that determines which validators qualify for the next round of block creation. Certain parameters of the weighting are variable and set by Core.
In November 2024, Core introduced Dual Staking, enabling BTC holders to multiply their rewards by simultaneously staking CORE tokens alongside their BTC. It also set the stage for lstBTC, a BTC liquid staking token that enables users to earn yield while retaining BTC liquidity in Core’s fully expressive execution environment. For a complete primer on Core, refer to our Initiation of Coverage report.
CORE is the native token of the Core blockchain and is used as the primary medium of exchange when transacting on the network. CORE has three additional primary use cases:
The total supply of CORE is fixed at 2.1 billion tokens. Block rewards are distributed over 81 years and decrease by 4% annually. CORE also has a minor deflationary burn mechanism to counteract inflationary pressure.
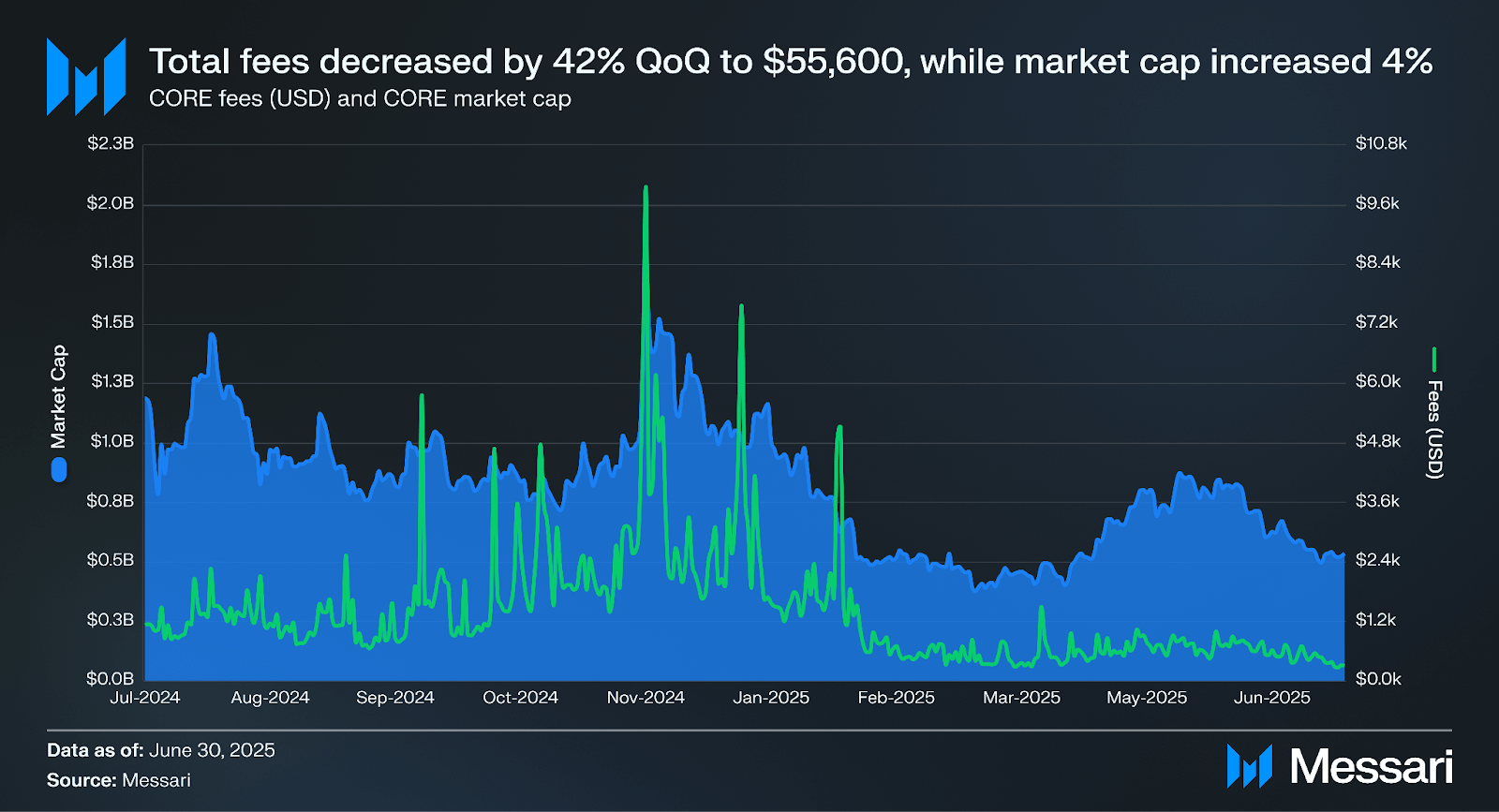
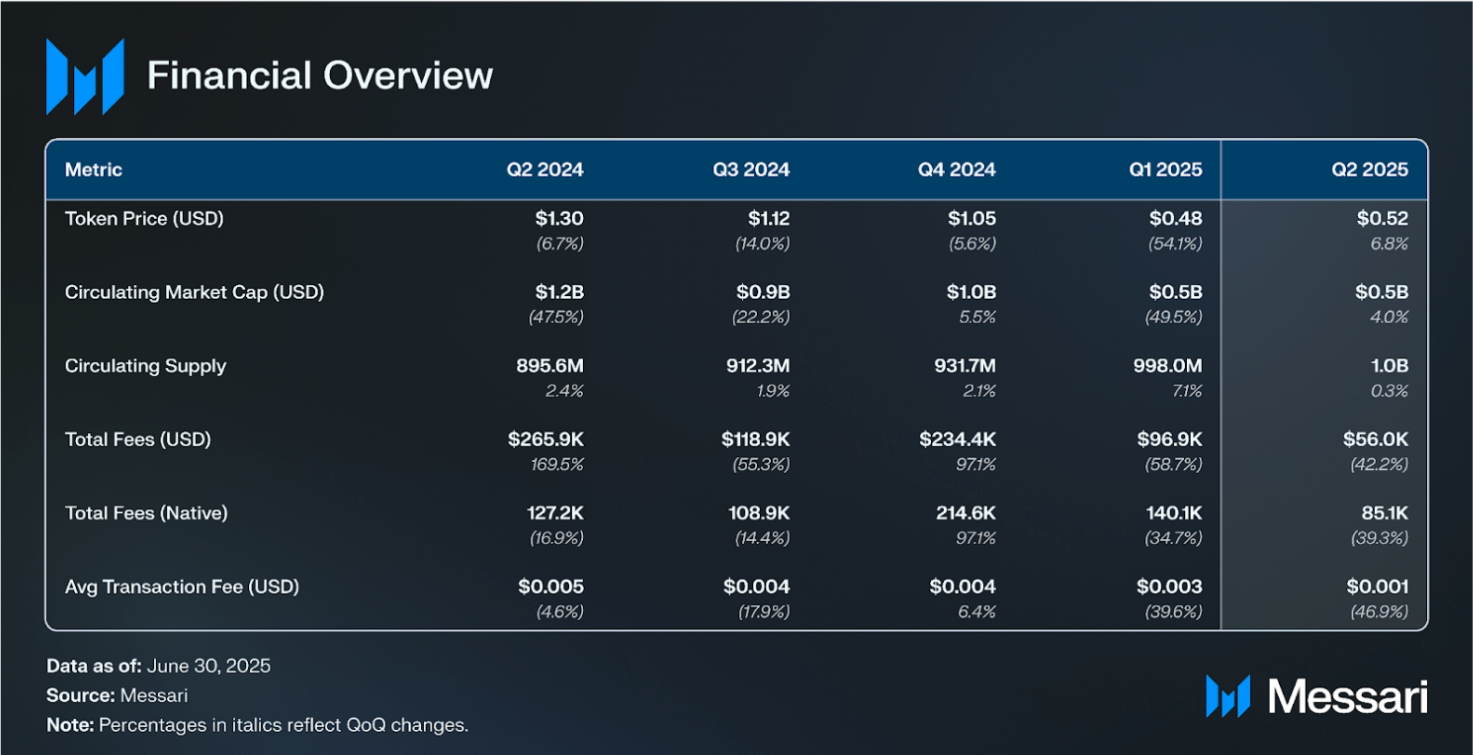
Total fees denominated in USD decreased by 42% QoQ to $55,600, while fees denominated in CORE decreased by 39% to 85,100. Core’s fees come from transactions on the network. This quarter’s fee decrease can be attributed to a 47% decrease in the average transaction fee (USD) on Core during Q2.
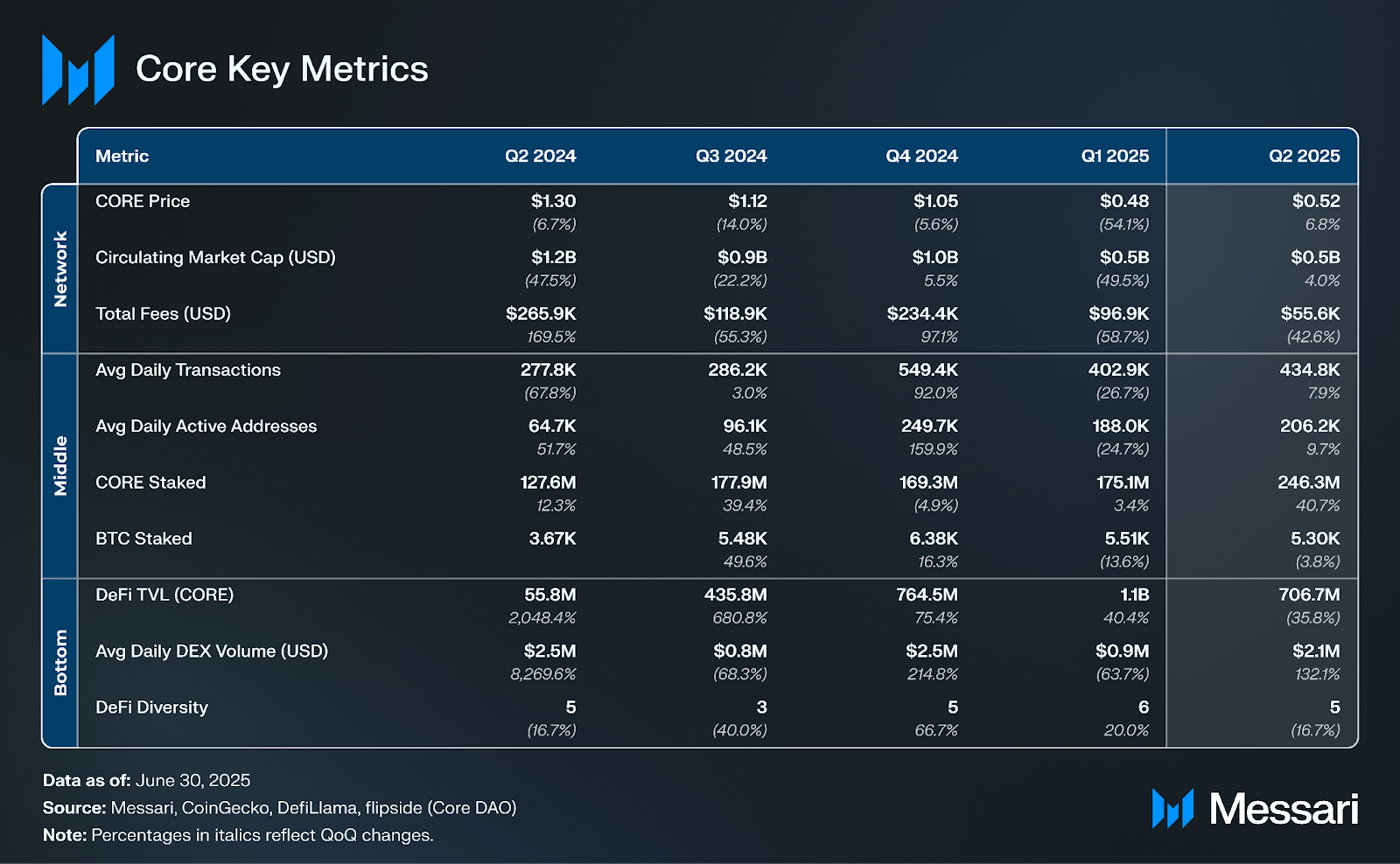
Core’s market cap increased by 4% QoQ to $514.0 million, while the CORE token price increased by 6.8% to $0.52, with the difference due to a 0.3% increase in the circulating supply of CORE. The market cap of all L1s (excluding Bitcoin) increased by 21% in Q2. In comparison, the market cap of Bitcoin sidechains increased by 10% in aggregate.
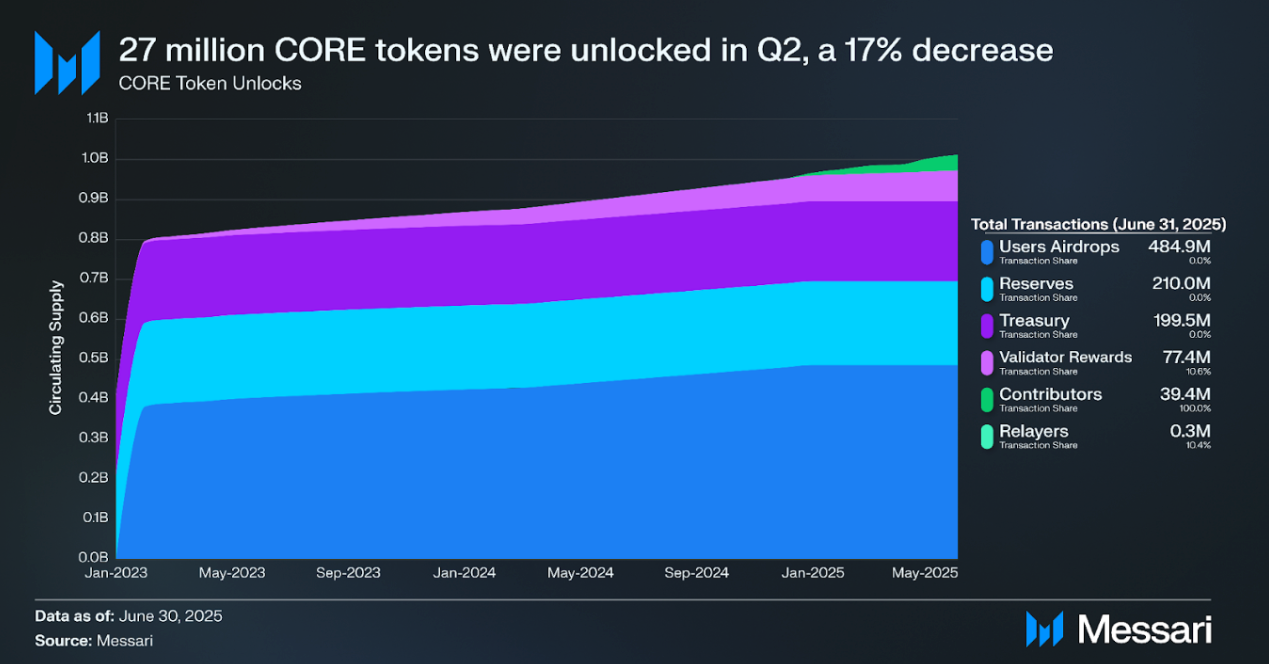
In Q2, 27.1 million CORE (3% of the total token supply) was unlocked. Of these, 7.4 million were for validator rewards, 19.7 million were for contributors, and 29,000 were for relayers. Contributor tokens were unlocked for the first time in Q2, and 6.6 million CORE will be unlocked monthly until the allocation is fully vested in 2029. The 484.9 million airdrop allocation became fully vested on Jan. 8, 2025.
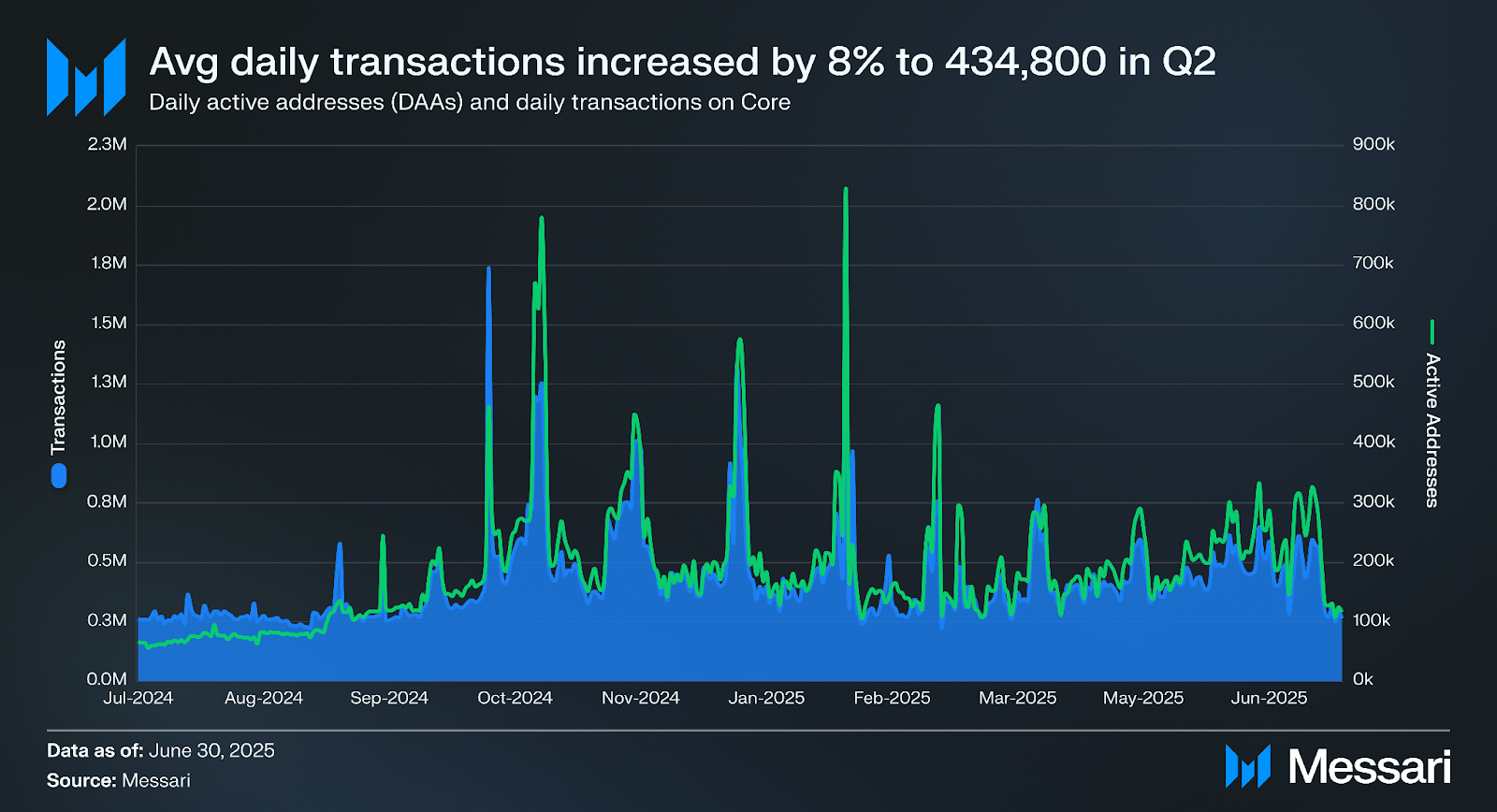
In Q2, average daily transactions increased by 8% to 434,800, while average daily active addresses increased 10% to 206,200. At the end of Q2, Core reached 59.1 million unique lifetime wallets, a 28% QoQ increase.
In Q2, the average block time on Core was only 3 seconds, whereas the average block time on Bitcoin was 10 minutes. Core is not limited by Bitcoin’s block time and can execute at an independent pace in any instance since the Core network is an independent L1.
At the close of Q2, Core had 30 active validators, a 14% increase QoQ. BitGo, Koda, and Luganodes joined as Core validators in Q2. Core uses its Validator Election Mechanism to rank the top 31 validators based on a weighted score of their hash, CORE stake, and BTC stake, creating the validator set for a consensus period of 200 slots, known as an epoch. In May 2024, Core DAO passed CIP-2 to expand Core’s active validator set from 21 to 31 by Q2 2025, which they’ve officially achieved after adding Blockdaemon in July 2025.
Core uses the novel Satoshi Plus consensus mechanism. Satoshi Plus is a hybrid model of Delegated Proof-of-Work (DPoW), Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS), and Self-Custodial BTC Staking. Unlike merge-mined sidechains, where multiple chains are mined simultaneously using the same computational resources, Core delegates the responsibility of producing new blocks to its validators, rather than Bitcoin miners.
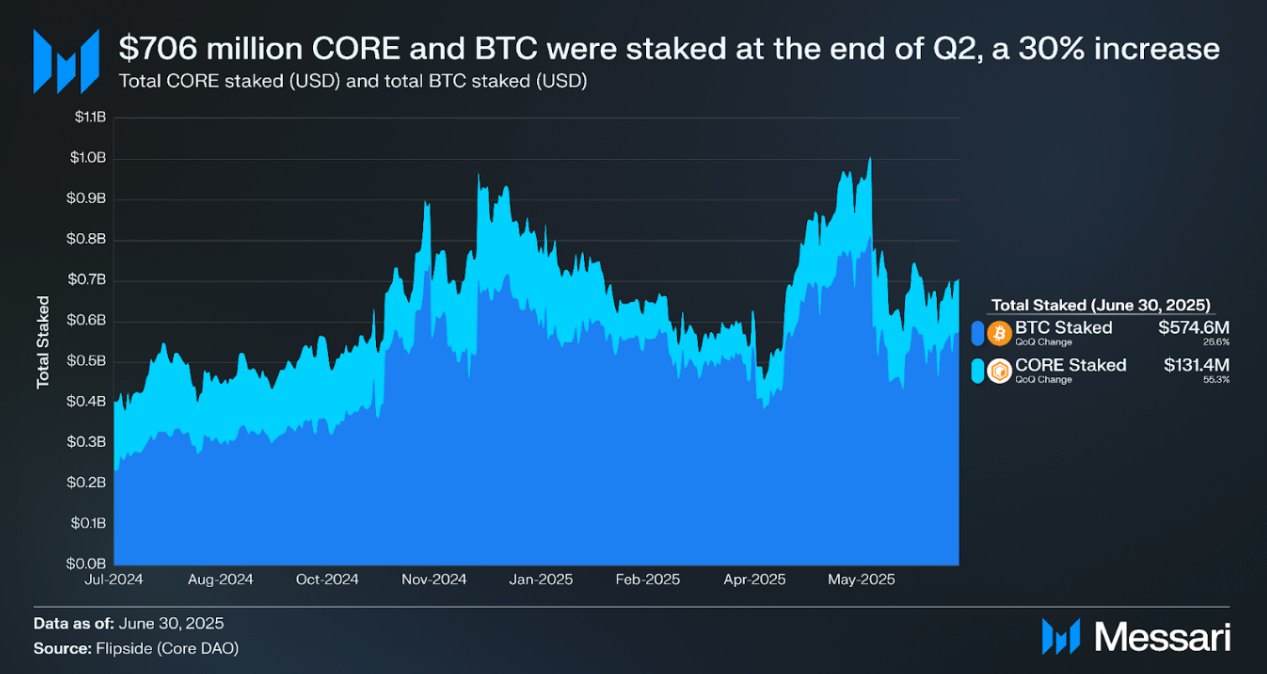
The total amount of CORE and BTC staked, denominated in USD, was $706.0 million at Q2 close, a 30% increase QoQ. CORE staked (USD) was up 55% QoQ to $131.4 million despite the token price only increasing 7% QoQ. CORE staked (native) increased 41% QoQ to 246.3 million.
BTC staked (USD) increased by 27% QoQ to $574.6 million at Q2 close, while BTC’s price increased 32% QoQ to $108,400. In contrast, BTC staked declined from 5,500 at the close of Q1 to 5,300 BTC at the close of Q2. BTC is staked (locked) through self-custodial BTC staking, which uses a CheckLockTimeVerify (CLTV) Timelock to lock BTC tokens on the Bitcoin network.
stCORE, Core’s native liquid staking product, launched in January 2024. stCORE enables CORE stakers to participate in DeFi and other yield opportunities while contributing to the Core blockchain. stCORE supply increased 22% QoQ to 18.3 million, equivalent to $12.4 million. Core had a 9% liquid staking rate at Q2 close, an 18% decrease from Q1. Liquid staking rate is the percent of liquid-staked CORE compared to total staked CORE, and can be used to measure ecosystem activity.
Dual Staking provides boosted CORE rewards to participants who stake both Bitcoin and CORE tokens (“dual stakers”), incentivizing BTC stakers to acquire and stake CORE to maximize their yield. This mechanism aims to enhance Core’s security by increasing the economic incentive to stake BTC and CORE.
The staking process remains unchanged, but reward allocation follows a tiered system. Previously, all BTC stakers received the same rewards rate, but under Dual Staking, rewards tiers are determined by the amount of CORE staked relative to BTC staked. The more CORE staked relative to BTC, the higher the rewards in that tier. While staking CORE introduces risks beyond holding BTC, the principal BTC holdings remain unaffected, as the BTC remains self-custodially locked on the Bitcoin network.
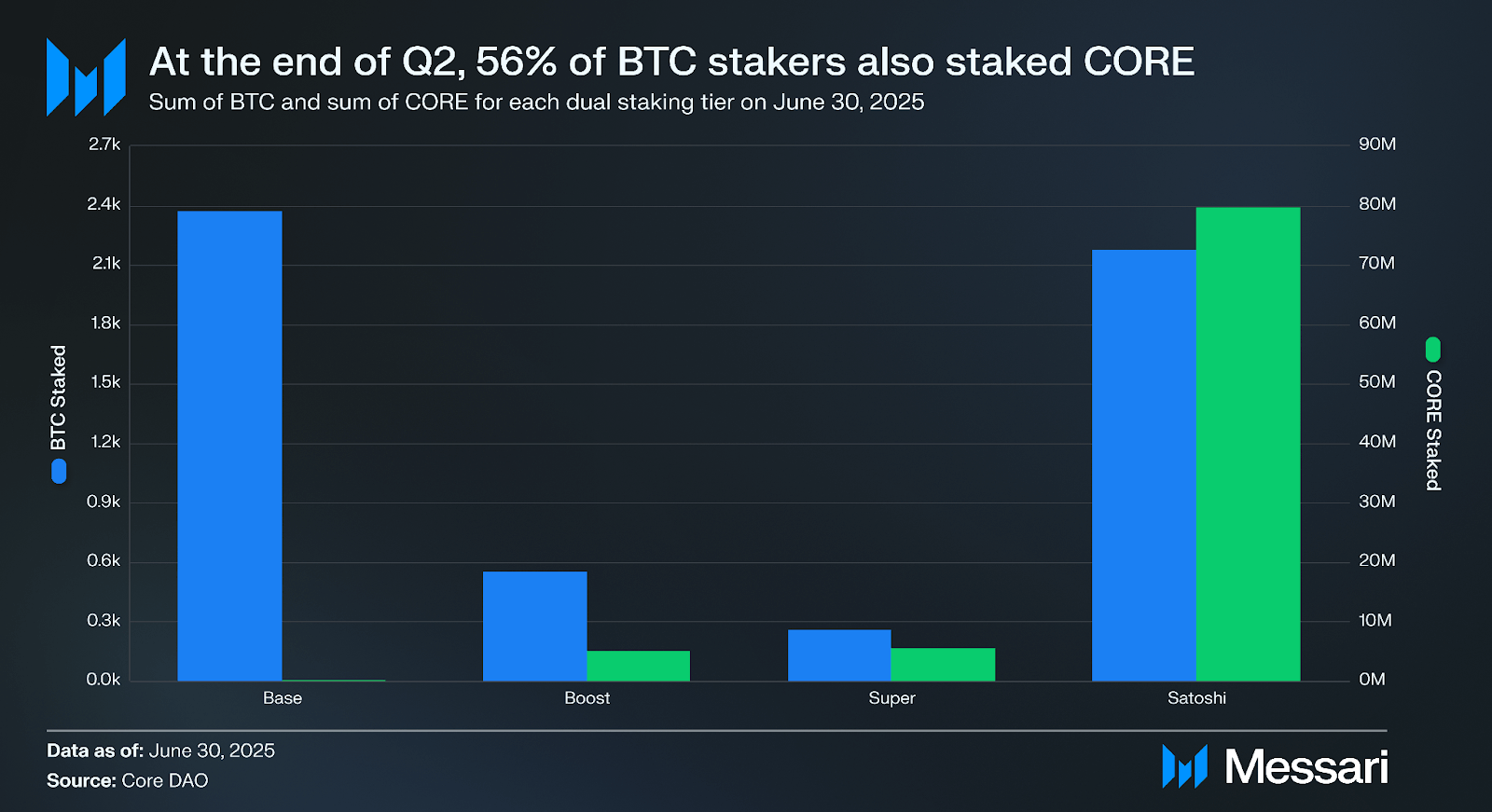
At the end of Q2, 56% of BTC stakers were also staking CORE, a 60% increase QoQ. Stakers can select from three tiers—Boost, Super, or Satoshi—determined by the ratio of CORE staked relative to their staked BTC. Higher tiers require more staked CORE to unlock greater yields. In Q2, Core DAO introduced two proposals to raise CORE staking requirements per tier, incentivizing BTC stakers to increase staked CORE commitments. The most recent proposal, CIP-6, increased CORE-to-BTC staking ratios by 42%, meaning the new requirements are:
41% of BTC dual-stakers were staking at the Satoshi tier at Q2 close, a 30% increase QoQ. Their combined CORE stakes account for 88% of all dual-staked CORE. Previously unstaked BTC moved disproportionately into the Satoshi tier compared to the Boost or Super tiers. This indicates a strong interest in dual staking to boost BTC yields and suggests BTC tokenholders are comfortable holding CORE to maximize their returns.
In February 2025, Core and Maple Finance announced the upcoming lstBTC token. lstBTC is an upcoming liquid staking token issued on the Core network representing staked BTC. Users who lock BTC on the Bitcoin network through Core’s CLTV contract receive lstBTC on Core. Maple Finance, a lending protocol, will borrow against some of the BTC for CORE tokens, which they will Dual Stake on Core.
The Core Foundation has also partnered with BitGo and Copper to expand lstBTC opportunities to institutional clients. Institutional BTC holdings are often less capital efficient. Profits are eroded by custody, leverage, and/or management costs. By adopting lstBTC, institutions can earn yield on top of their BTC, unlocking potentially greater returns for themselves and their stakeholders. lstBTC enables participation in activities like lending, liquidity provision, borrowing stablecoins for trading, or engaging with various BTCFi apps. As of the end of Q2, interested parties can join the waitlist to access lstBTC.
The Theseus Hardfork is a major network upgrade for Core, which activated on June 25. It introduced two key features: transaction hooks and protocol-level fee sharing.
Additionally, Theseus added support for pre- and post-transaction hooks, which allow developers to attach custom logic that runs immediately before or after a transaction executes. Pre-transaction hooks can enforce conditions or validations, while post-transaction hooks can log events, route fees, or trigger follow-up actions without modifying the core contract logic.
Fee sharing will enable a portion of gas fees to be redirected to smart contract developers, DAOs, or other governance-designated recipients, creating a direct incentive to build and maintain onchain infrastructure. According to Core, fee sharing is set to go live in H2 2025.
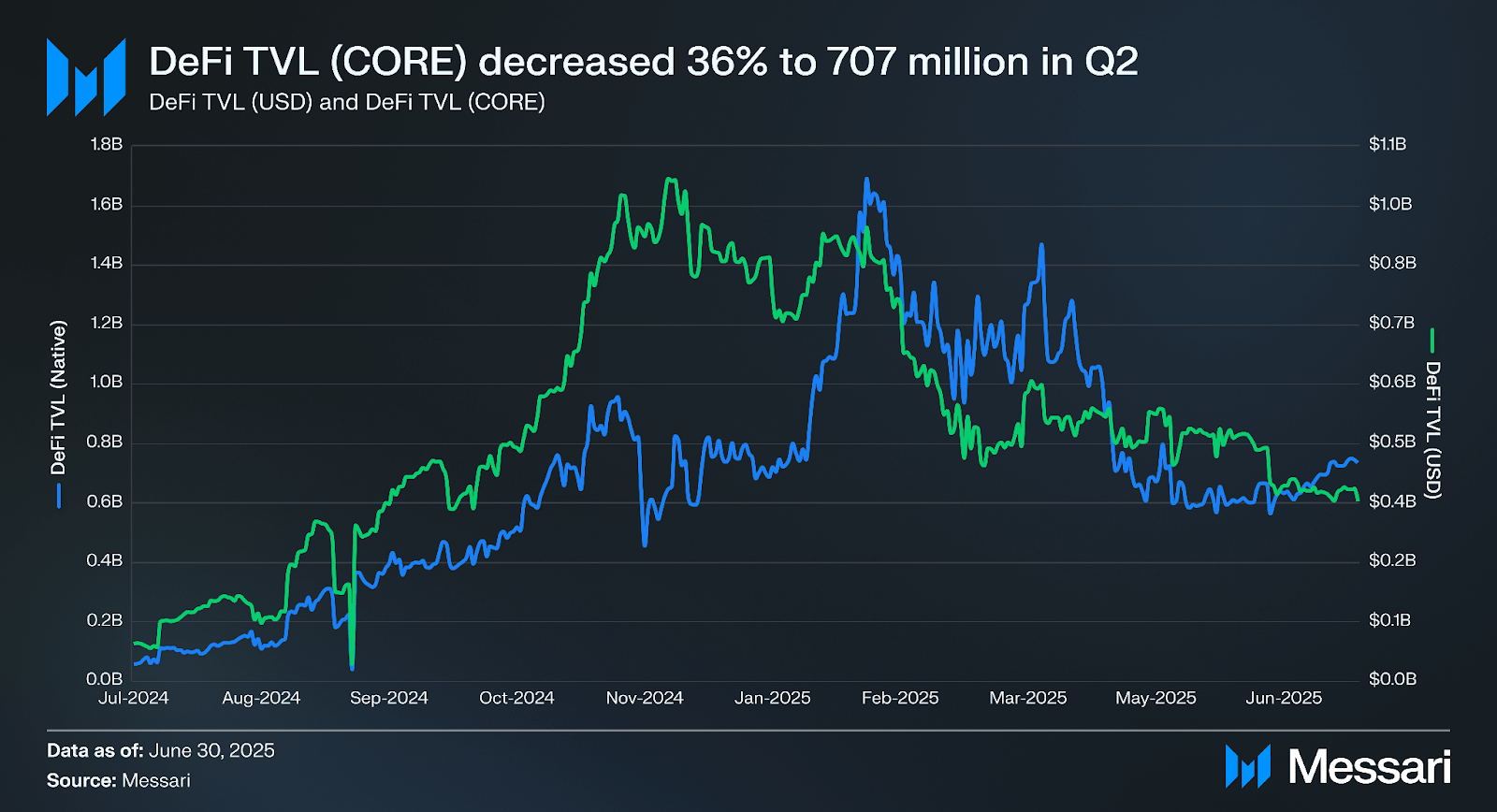
DeFi TVL denominated in CORE decreased 36% QoQ to 706.7 million at Q2 close, while DeFi TVL denominated in USD decreased 31% to $394.1 million. The discrepancy is due to the CORE token price increasing 7% QoQ from $0.48 at Q1 close to $0.52 at Q2 close.
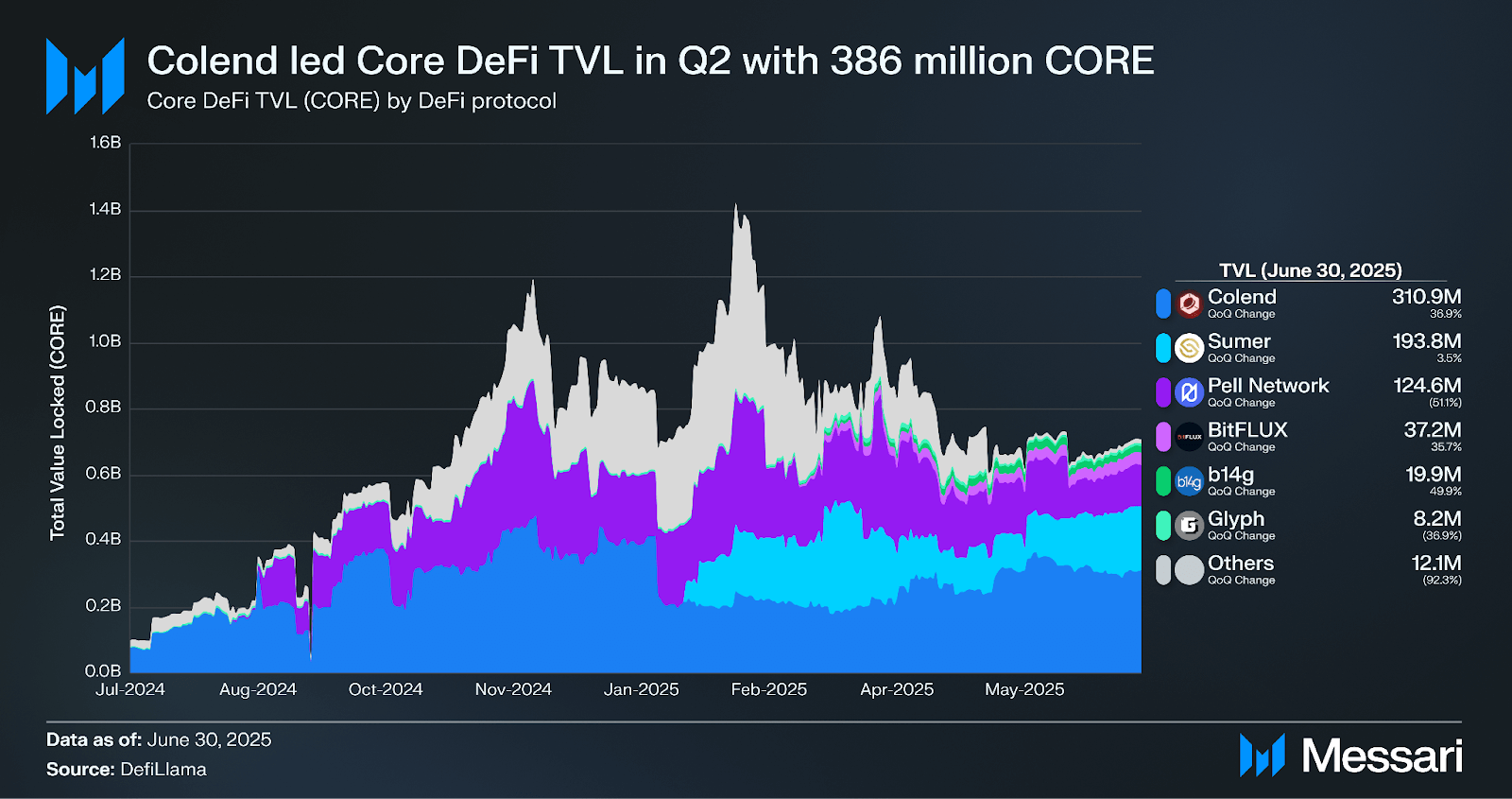
At Q2 close, Colend remained the dominant DeFi application on Core with 310.9 million CORE in TVL, up 37% QoQ. SolvBTC.CORE, a wrapped version of BTC custodied by Solv, was the largest contributor to Colend’s TVL with 227.2 million CORE in TVL, equivalent to $113.6 million.
Sumer is a multichain synthetic asset and lending protocol forked from Compound V2. The synthetic assets (SuUSD, SuETH, and SuBTC) are backed by collateral from lending markets. Sumer launched on Core on Jan. 6 and ended Q2 with 193.8 million CORE in TVL, up 3.5% QoQ.
Pell Network, a Bitcoin restaking layer, was the second-largest application behind Colend at the end of Q2 with 124.5 million CORE in TVL, a 51% decrease QoQ. Pell announced their $2.5 million raise on Jan. 27, in which Core Ventures participated. Pell airdropped their token on March 13.
BitFLUX (rebranded to Molten Finance in Q3) is a stableswap DEX on Core designed for low-slippage swaps between BTC-pegged assets. It enables single-sided liquidity provision, letting users earn yield on BTC without impermanent loss risk. BitFLUX’s TVL rose 36% QoQ to end Q2 at 37.2 million CORE.
b14g is a dual staking protocol that lets users stake BTC and CORE together to earn higher, auto-compounding yields. It uses liquid staking tokens like dualCORE to provide yield-bearing exposure with onchain composability. b14g ended Q2 with 19.8 million CORE, a 50% increase QoQ.
DeFi diversity represents the number of protocols that make up >90% of DeFi TVL. Core’s DeFi diversity was 5 in Q2, with TVL concentrated in Colend, Sumer, Pell Network, BitFLUX, and b14g.
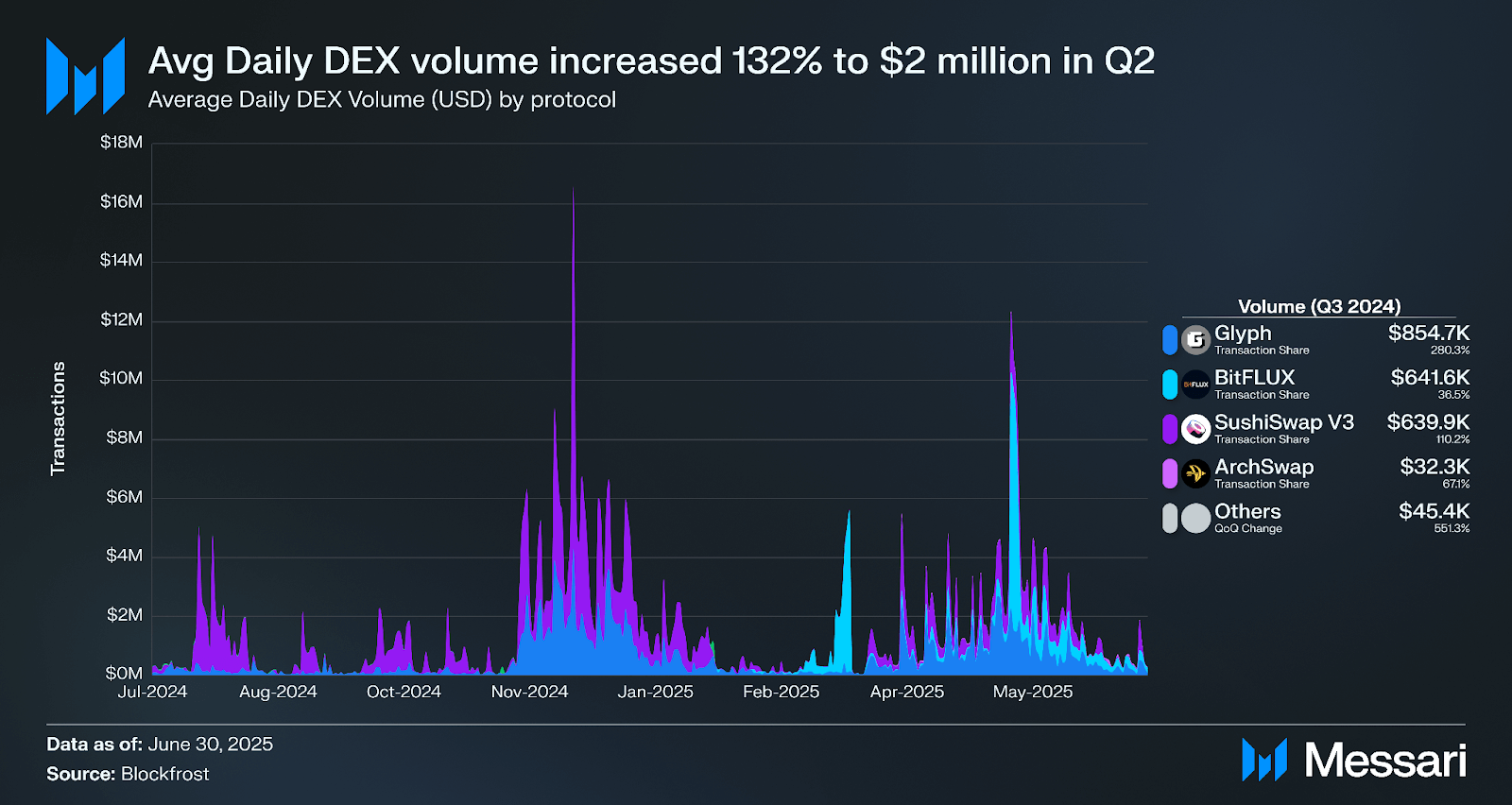
Volume on BitFLUX spiked to $10.0 million on May 10 following an announcement of a 50x Sparks (loyalty points on Core) multiplier.
In May 2024, Core DAO updated the Core Ignition incentive program to introduce Sparks to measure and reward user activity and engagement. Sparks are synonymous with the points several popular pre-airdrop protocols began offering over the past year.
Users receive a daily allocation of Sparks, determined by their level of engagement and participation in the Core ecosystem. The more active and involved a user is, the greater their daily allocation of Sparks will be. Additionally, Core offers a multiplier on specific assets that adjusts your conversion rate (i.e., if you hold an asset with a 1.5x multiplier and earn 100 base Sparks a day, you’ll receive an additional 50 Sparks a day through the asset multiplier).
On March 12, Core launched Season 3 of Core Ignition, resetting Sparks to 0 for all participants. Season 3 introduced new multipliers to earn Sparks through Core network applications, bridging, and trading. Core also launched an Ignition Leaderboard to track Spark Points. As of Q2, Season 3 is active, with incentives for protocols like BitFLUX, Nawa Finance, and Colend.
In June 2025, Core DAO announced its H2 2025 Roadmap:
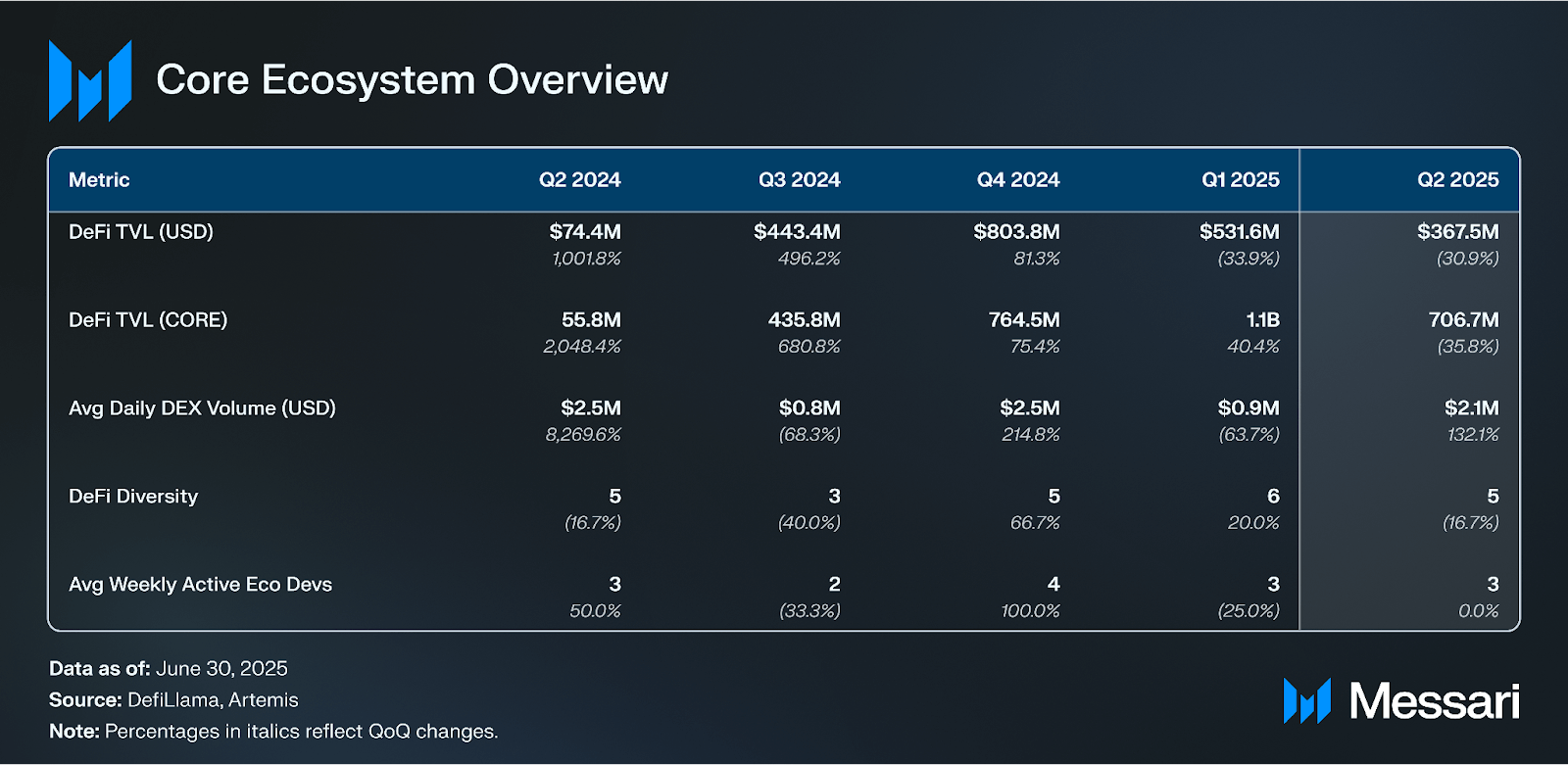
In Q2 2025, Core’s native DeFi TVL declined 36% to 706.7 million CORE, and 31% in USD terms to $367.5 million, despite a 7% increase in CORE’s token price to $0.52. Market cap rose 4% QoQ to $514.0 million, driven by a 0.3% increase in circulating supply. Network activity strengthened, with daily transactions up 8% QoQ to 434,800 and active addresses rising 10% to 206,200. Average daily DEX volume rose 132% QoQ to $2.1 million. Total BTC and CORE staked increased 30% to $706.0 million, with BTC staked down 4% to 5,300 and CORE staked up 41% to 246.3 million.
Dual Staking adoption increased, with 56% of BTC stakers also staking CORE, and 88% of dual-staked CORE allocated to the top Satoshi tier. Core activated the Theseus Hardfork in late June, introducing fee sharing and contract hooks to improve developer incentives and execution flexibility. Sparks Season 3 continued with DEXs such as BitFLUX showing signs of success from the incentive program. DeFi usage remained concentrated in protocols like Colend, Sumer, and b14g. Looking ahead, Core is preparing to launch lstBTC, integrate a major stablecoin, expand hardware wallet support, and introduce new staking mechanics, validator revenue sharing, and local fee markets to strengthen its infrastructure and token utility.
Let us know what you loved about the report, what may be missing, or share any other feedback by filling out this short form. All responses are subject to our Privacy Policy and Terms of Service.
This report was commissioned by Core DAO. All content was produced independently by the author(s) and does not necessarily reflect the opinions of Messari, Inc. or the organization that requested the report. The commissioning organization may have input on the content of the report, but Messari maintains editorial control over the final report to retain data accuracy and objectivity. Author(s) may hold cryptocurrencies named in this report. This report is meant for informational purposes only. It is not meant to serve as investment advice. You should conduct your own research and consult an independent financial, tax, or legal advisor before making any investment decisions. Past performance of any asset is not indicative of future results. Please see our Terms of Service for more information.
No part of this report may be (a) copied, photocopied, duplicated in any form by any means or (b) redistributed without the prior written consent of Messari®.